Digital Certificate
A digital certificate validates authenticity between a website and a user, company, or similar identity. Say with more technicalities:
An electronic file tied to a cryptographic key pair authenticates the identity of a website, individual, organization, user, device, or server.
It served to show, that someone is responsible for the website, which significantly reduces the risk when browsing it. In case of problems, falsification, or theft of data, "someone" should be held responsible.
How do they work?
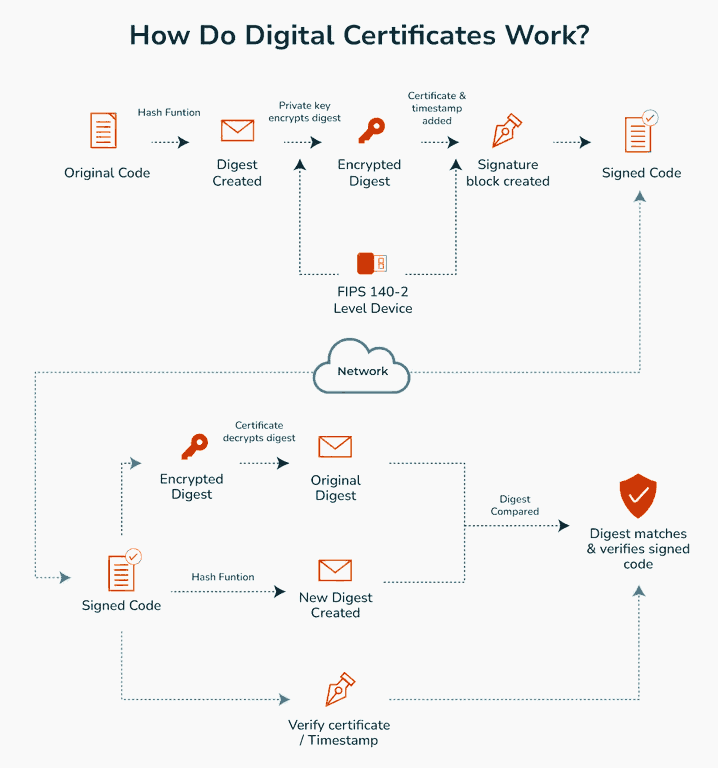
Its functioning is similar to an ID card used to prove someone’s identity or to secure a connection.
Issuance by a Trusted Authority: A trusted organization called a Certificate Authority (CA), like Verisign or Let’s Encrypt, issues the certificate. They verify the identity of the entity requesting it (usually a website or a person) before issuing the certificate.
Encryption and Keys: The certificate has a pair of "keys" – a public key and a private key. The public key is shared with anyone who wants to connect securely to the certified entity, while the private key is kept secret by the certificate holder.
Securing Data Transfer: When you connect to a site with a digital certificate, your data is encrypted with the site’s public key. Only the site’s private key can decrypt it, so it stays secure from others.
Authentication: The digital certificate also authenticates the identity of the site. Your browser checks that the certificate is valid and signed by a trusted CA. If it is, your browser trusts the site and lets you connect securely.
Expiration and Renewal: Certificates expire after a certain period (not more than 27 months) and need to be renewed, ensuring that the information stays up-to-date and secure.
In summary, a digital certificate assures users that they are communicating with the right entity and that their information is protected during transmission.
Types:
Extended Validation EV SSL: This provides comprehensive business authentication, which is necessary for handling extremely sensitive data for businesses or larger organizations. It’s a priority in the financial sector because it provides the highest degree of trust, security, and authenticity.
Client Certificate: A client certificate is a digital identity that uniquely identifies a person to another user, computer, or machine to another. Email is a typical example of this, in which the sender digitally signs a message, and the receiver verifies the signature. This is the most effective way to verify the certificates.
Code Signing Certificate: This is required to verify the legitimacy of software or files obtained from the internet. Is proof that software is authentic. Especially helpful when using external websites as providers.
TLS/SSL Certificate: A program, mail, or web server, for example, uses a TLS/SSL certificate to guarantee and secure encrypted and confidential communication with its customers. The certificate gives the server the authentication it needs to transmit and receive encrypted communications to clients.
Domain Validated DV SSL: Any website can use a quick validation technique that works with a domain-verified certificate. It is inexpensive to get and is ready to use in a few minutes.
How can they help me or my Business?
The main reason is to avoid anyone replicating your website. Ensures that all the information is encrypted, especially important when the user must log in or add their bank details and other sensitive information.
Furthermore, if your website does not have one of these certificates, it is very likely that the browsers and search engines themselves are likely to make your website invisible in order to prioritize user security. This is going to happen even if you have a certificate but it expired. Keeping the expiration date in mind can prevent a major SEO disaster.
In the same way, it is important to avoid accessing any site that does not have this certificate, for our own security or that of our business.
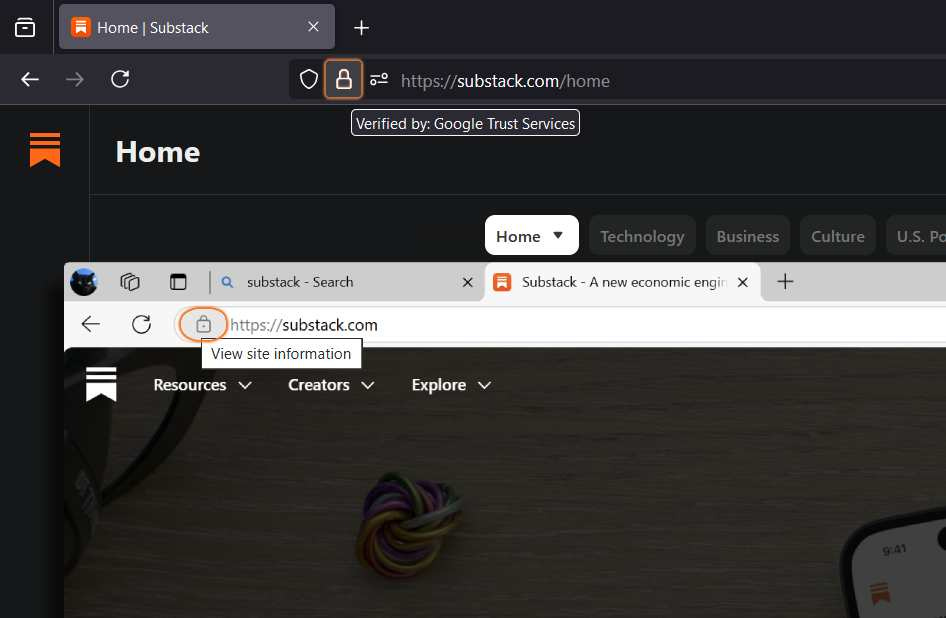
How do I know if a website has it?
You should be able to see a padlock symbol in the top corner of the browser, additionally, it will warn you that the connection is secure, and will use HTTPS instead of HTTP:
Normally to apply these certificates, the server where your website is hosted, should show an option inside of the cPanel. Here, we can use our key or demand a new one. By default always is important to have the SSL for (HTTPS) activated, if it’s not yet.